Diabetic Eye Exams


What Is
Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition that can involve the eyes just like other organs in the body. The chance of having diabetic complications in the eye is directly related to how uncontrolled diabetes is and how long the patient has had it.
In addition, concurrent high blood pressure can also increase the chance of getting diabetes-related eye problems. Because of the possible occurrence of diabetic eye complications, the American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends yearly diabetic eye exams for all Type I and Type II diabetics.
Refractive Error
Fluctuating blood sugars can make the lens in the eye swell and therefore change its ability to focus properly. This can cause frequent changes in glasses prescriptions and episodes of blurry vision. When your ophthalmologist performs a complete diabetic eye exam, this refractive error can be detected. The best treatment is tight blood sugar control rather than continuing to change glasses prescriptions.
Cataracts
Elevated blood sugar can cause the formation of cataracts or accelerate the growth of pre-existing cataracts. Often, these cataracts do not completely go away even with tighter sugar control.
Symptoms:
- A gradual, painless decrease in vision
- Double vision or distorted vision
- Glare from headlights or on bright days
- Difficulty reading
- Difficulty driving due to glare or blur
- No vision improvement with glasses adjustment
Diagnosis
A comprehensive dilated exam including refraction and bright light testing (BAT) is necessary to diagnose cataracts, assessing the degree of cataract formation is important in deciding the next step.
Treatment
Cataract surgery has undergone incredible changes over the last 20 years. It is now performed on an outpatient basis with a stitchless micro-incision technique that takes only 20-30 minutes. It is important to remember that after surgery, diabetic patients can have slower wound healing and a higher risk of swelling in the back of the eye.
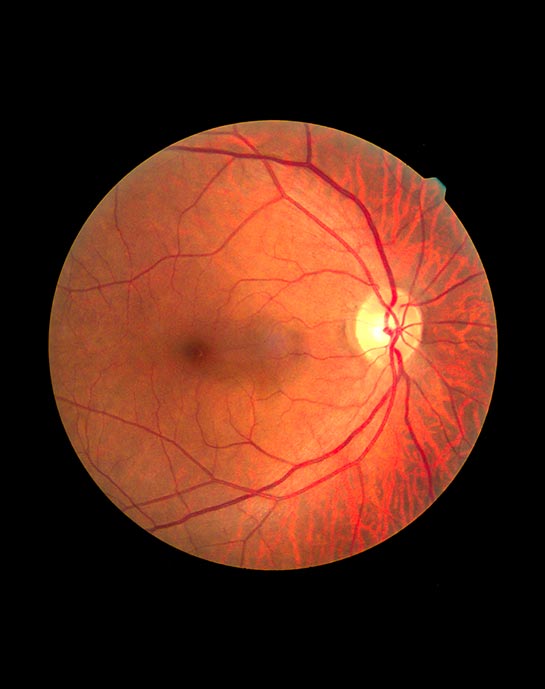
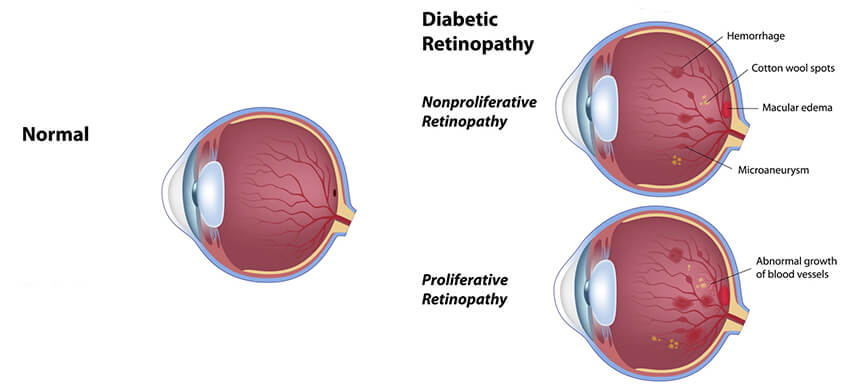
Diabetes can also affect the blood vessels of the back layer of the eye or the retina. Chronically elevated blood sugars cause three main problems in the retina:
- Leaky blood vessels which cause swelling in the back of the eye
- Fragile, abnormally growing blood vessels which cause bleeding and vision loss
- Detachment of the retina due to traction caused by these abnormal blood vessels
Symptoms:
- A gradual, painless decrease in vision
- Distortion in central vision
- Difficulty reading or driving
- New flashes or floaters,”spider webs” in the vision
- Sudden onset of painless, decreased vision
Diagnosis:
- Dilated eye exam: this is the main modality used to find diabetic retinopathy, a lens is used to examine the retina, and swollen areas or bleeding can be directly seen by your ophthalmologist
- Fluorocein Angiogram: this is a photographic test in which a synthetic dye is injected into the arm vein, and the retina is photographed as this dye travels through the retinal blood vessels; swelling and subtle areas of bleeding can be seen
- Vision testing
- Visual field testing
Treatment:
- Blood sugar and high blood pressure control
- Eye drops for reduction of retinal swelling
- Eye drops for reductioSteroid injections for retinal swellingn of retinal swelling
- Retinal laser for treatment of abnormal blood vessels and bleeding
- Retina surgery for large areas of bleeding that don’t resolve on their own
- Retina surgery of diabetes-induced retinal detachment
Request A
Consultation
To request a consultation with Westlake Eye Specialists, please click link below.

